softmax function
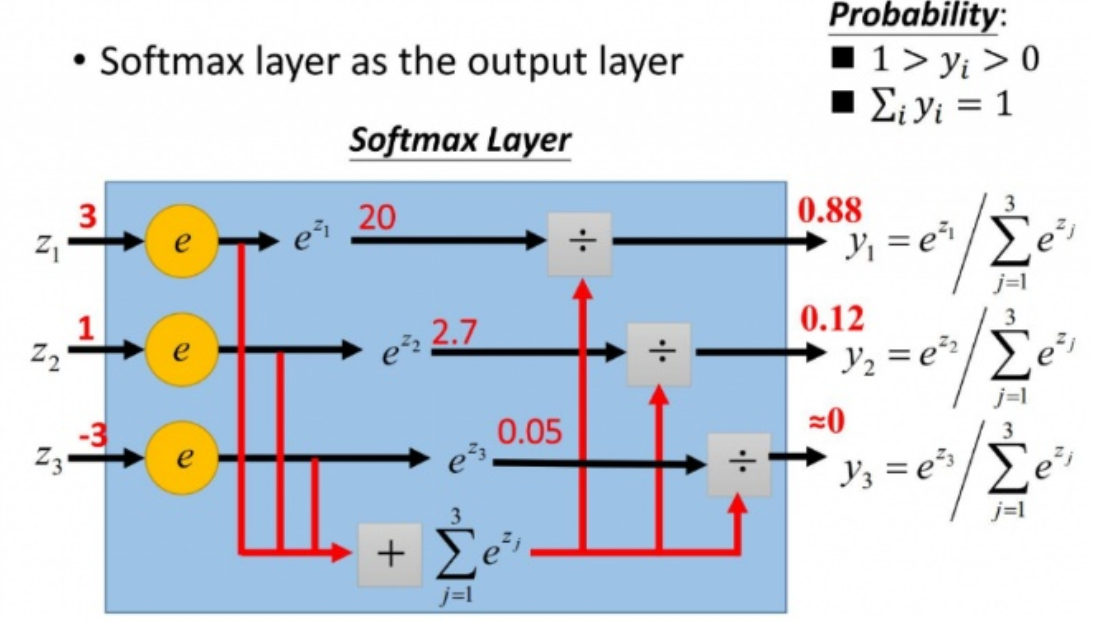
softmax is used to to transform multi-output values in (0, 1) zone, so that a proper selection according to max. probability can be made
the mathmatical expression is shown:
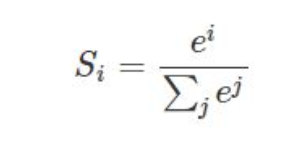
loss and gradient
the loss is expressed with cross-entropy function:
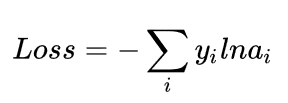
y: true value
a: predicted value with softmax
Partial derivative
if j not equal i: aj
if j equal i: ai-1
[i is the final selected one;
j is the item to derivate partially]
implementation
logits: the non-normalized probability y=tf.matmul(x,w)+b
-
tf.nn.softmax(logits, name=None)
y_hat=… #predicted label, e.g. y=tf.matmul(x,w)+b y_true=.. #label, one_hot encoded y_hat_softmax=tf.nn.softmax(y_hat) total_loss=tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_true*tf.log(y_hat_softmax), [1]))
-
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None)
label is one-hot coded
this only backwards update the logits total_loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(y_hat, y_true))difference to sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits is that sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits can calculate cross entropy of independet but not mutually exclusive (multi-class) targets; one class target classification sis not feasable for sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits; the input logits is not processed with sigmoid
-
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits, labels, name=None)
label is on-hot coded this will update logits and labels in backwards propagation, e.g. GAN. the propagation to labels can be deactivated by graph.stop_gradients(labels)
-
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None)
labels is the label index, not one-hot coded array
so
labels_not_hot_coded=tf.argmax(labels_hot_coded, 1) => tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels_not_hot_coded)=tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, tf.argmax(labels_hot_coded, 1))