this artical will introduce 14 common algorithm modes
sliding window
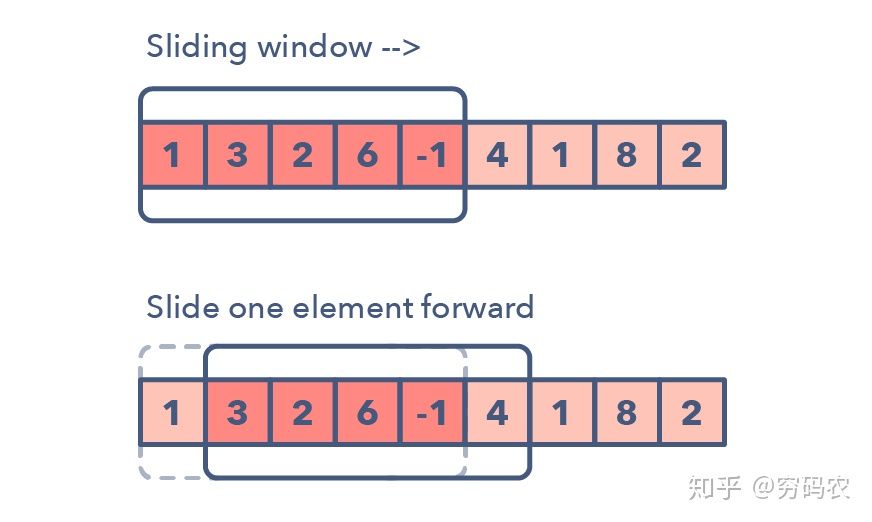
sliding window usually used to solve probelm:
- max sum of sub-array with size of K
- longst sub-string with K different letters
- find word in string
double pointers
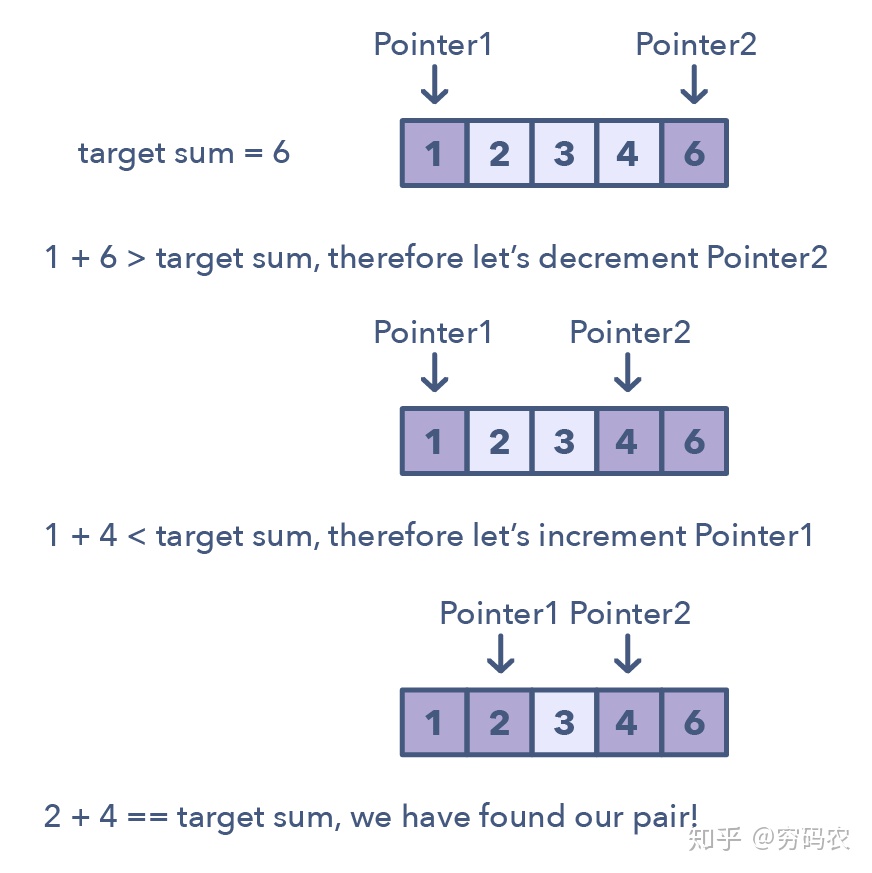
double pointer used to solve problem with restractions in ordered array or linked list
- Given an array S of n integers, are there elements a, b, c in S such that a + b + c = 0? Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero
- check equality of two strings
fast-slow-pointer
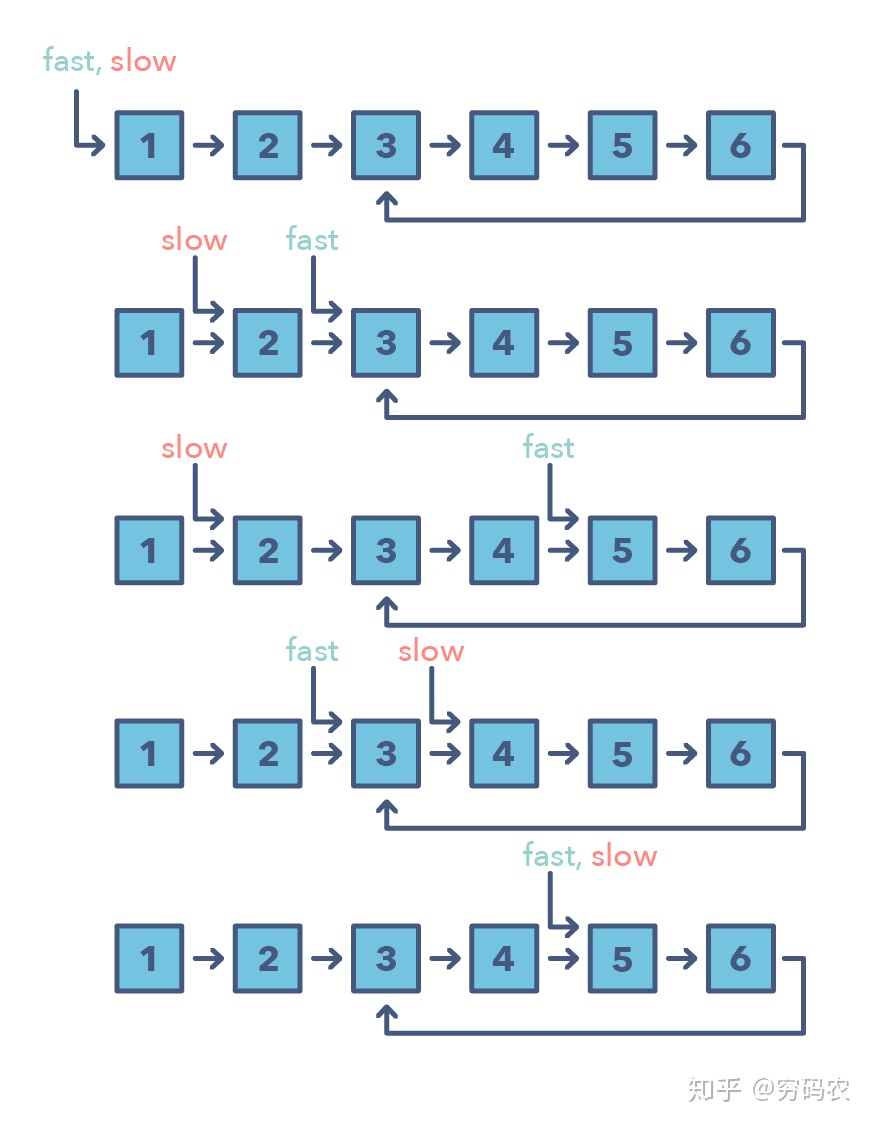
fast-slow-pointer used to solve problem for array cycle or linked list cycle
- check cycle in linked list
- check Palindrome in linked list
- find cycle in array cycle
## Interval merge
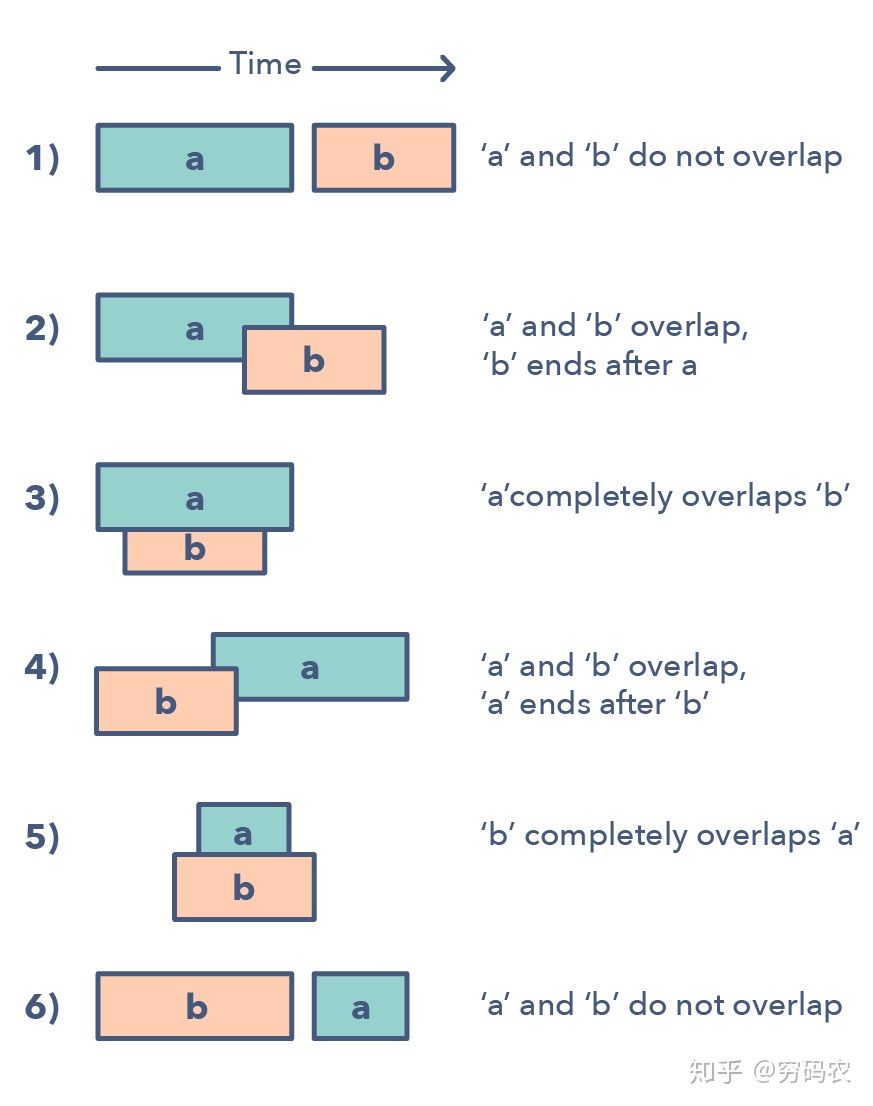
interval merge used to solve insert or merge in interval problem
- Interval intersection
- Maximize CPU load
cycle sorting
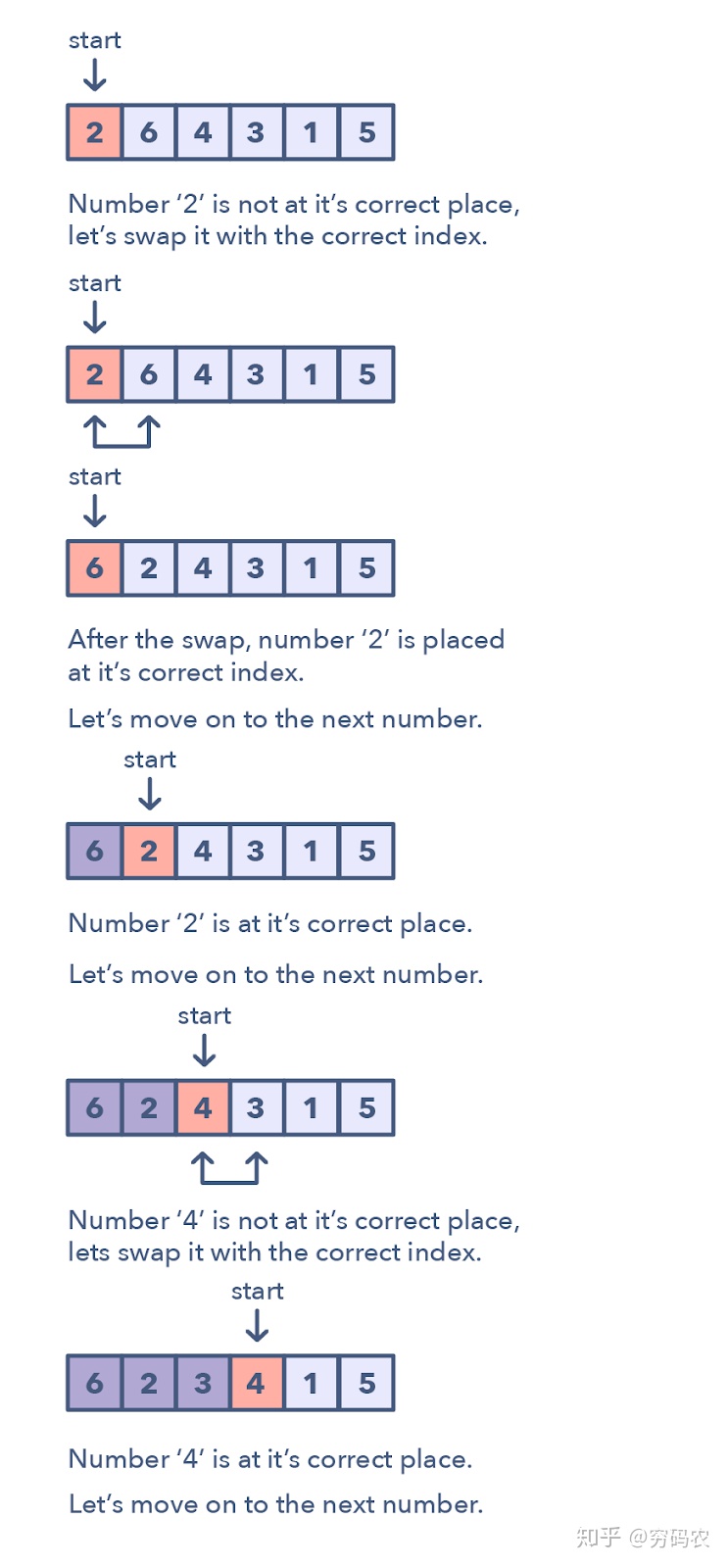
cycle sorting used to solve problem that in ordered array in specified range
- find digital not existing in array
- find min. number not existing in array
linked list flip
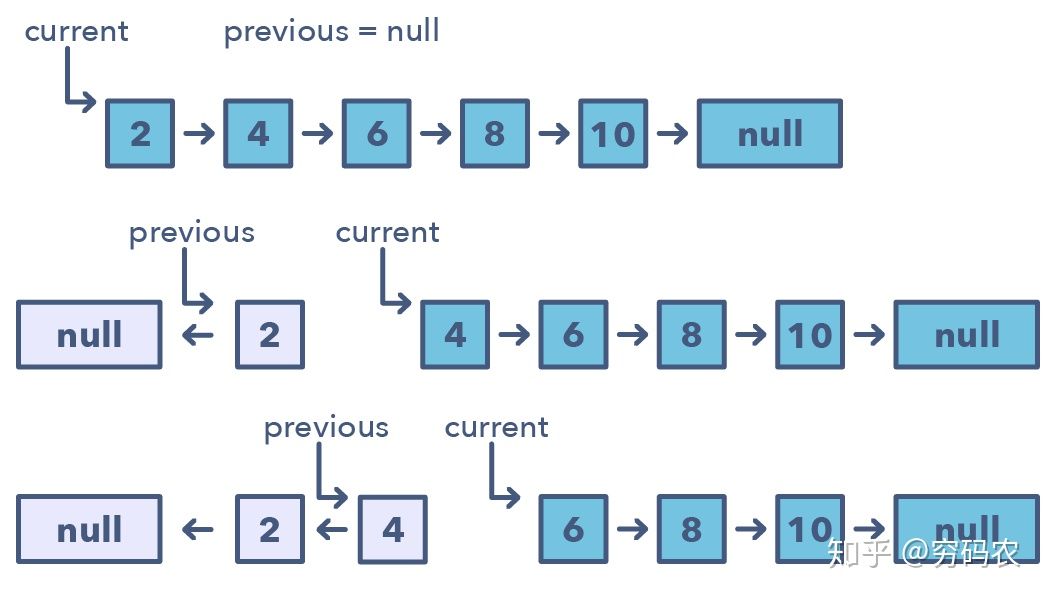
fliping used to solve linked list problem without extra memory
- Flip part of linked list
- Flip sub linked list with size K
BFS tree
BFS to search over a tree over layer
- binary tree sequence search
- zigzag search
DFS tree
DFS used to solve problem that has a solution near leaf node
- digital sum of all path on tree
- all paths the have a defined sum
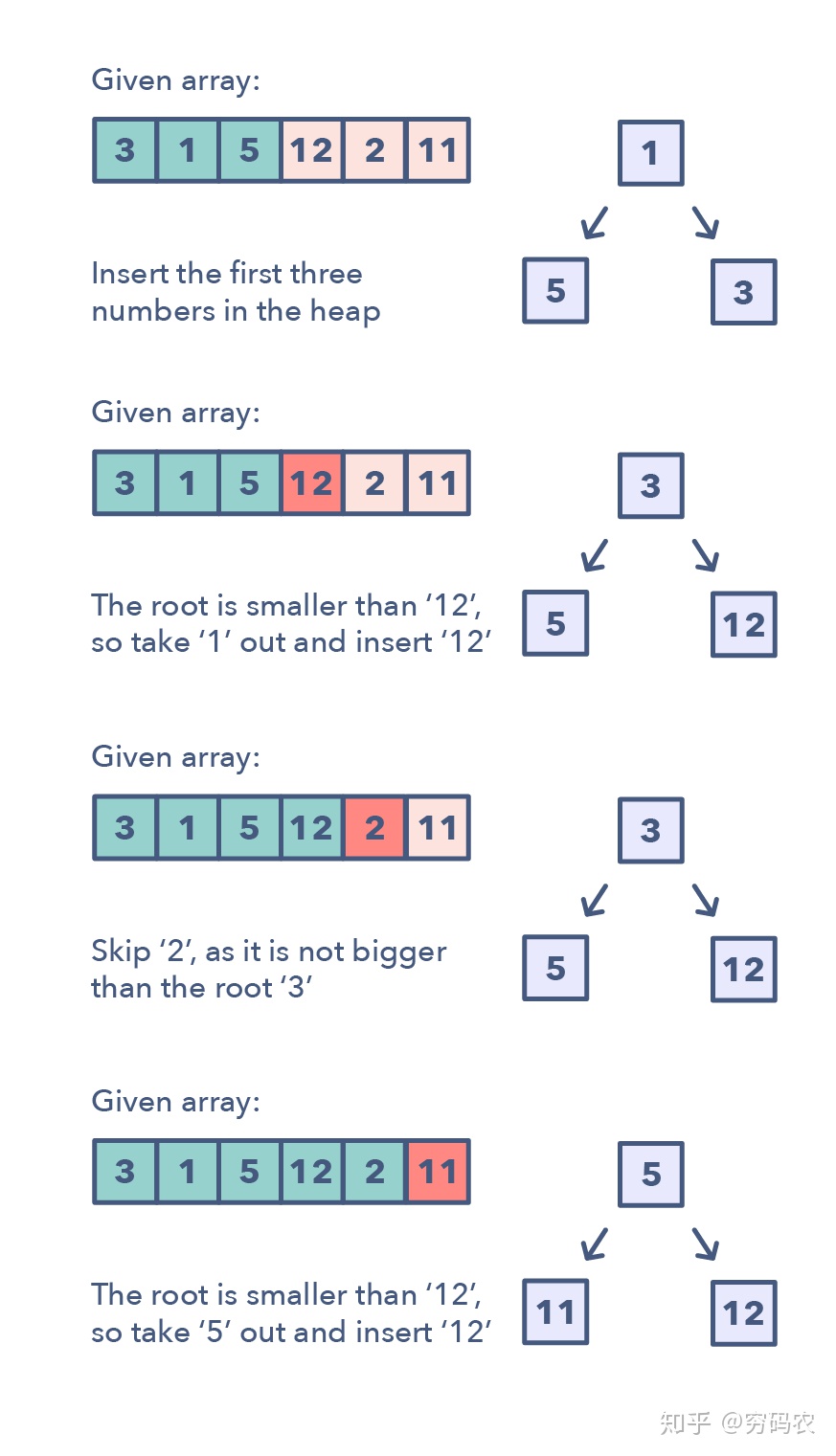
Double heap
- scheduling problem
- find max, min or medium
Sub-set
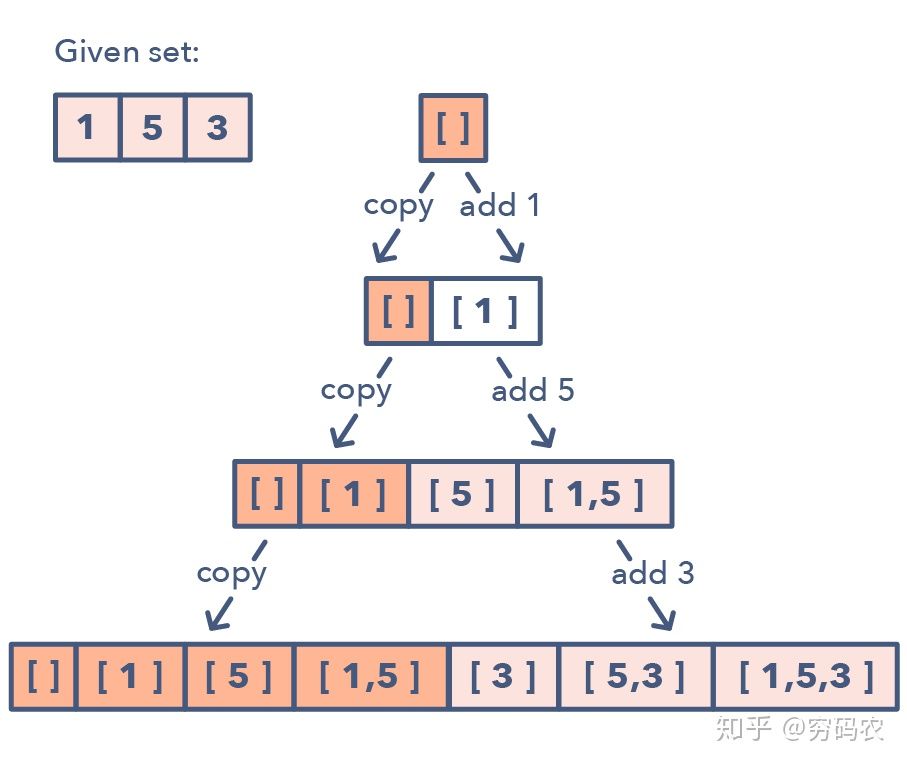
used to solve problem in Permutation and combination
- All subsets with repeating elements
- find all permutation with changing case
binary search variant
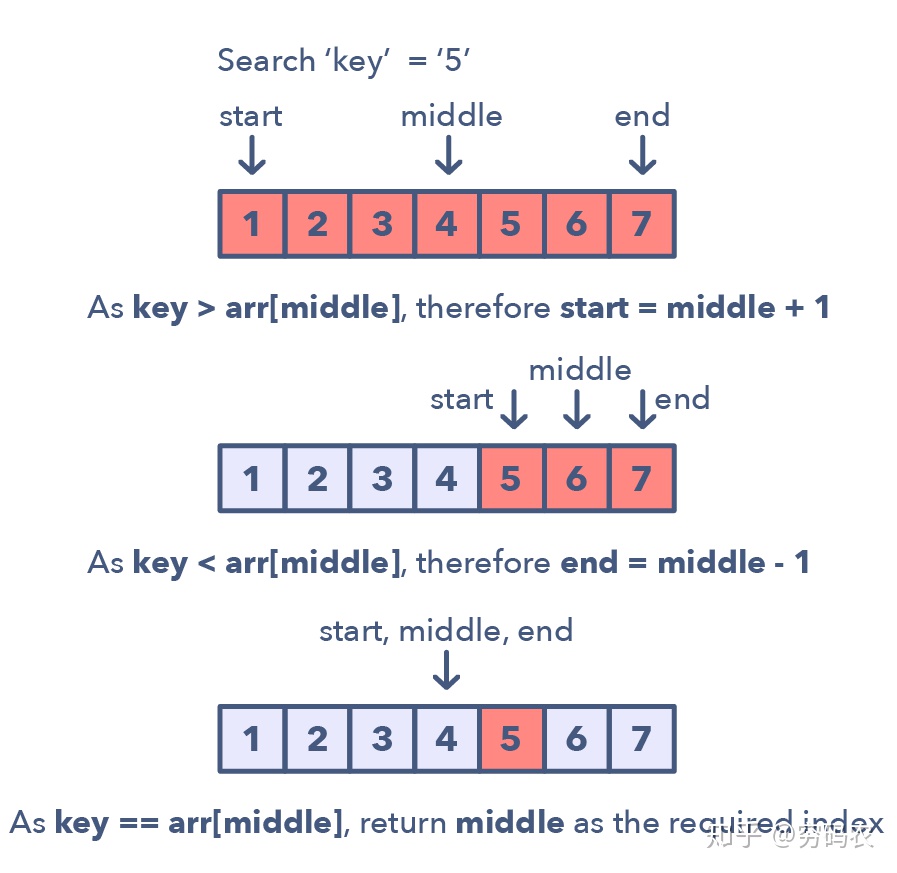
find k max
data structure is heap or priorityqueue
K merge
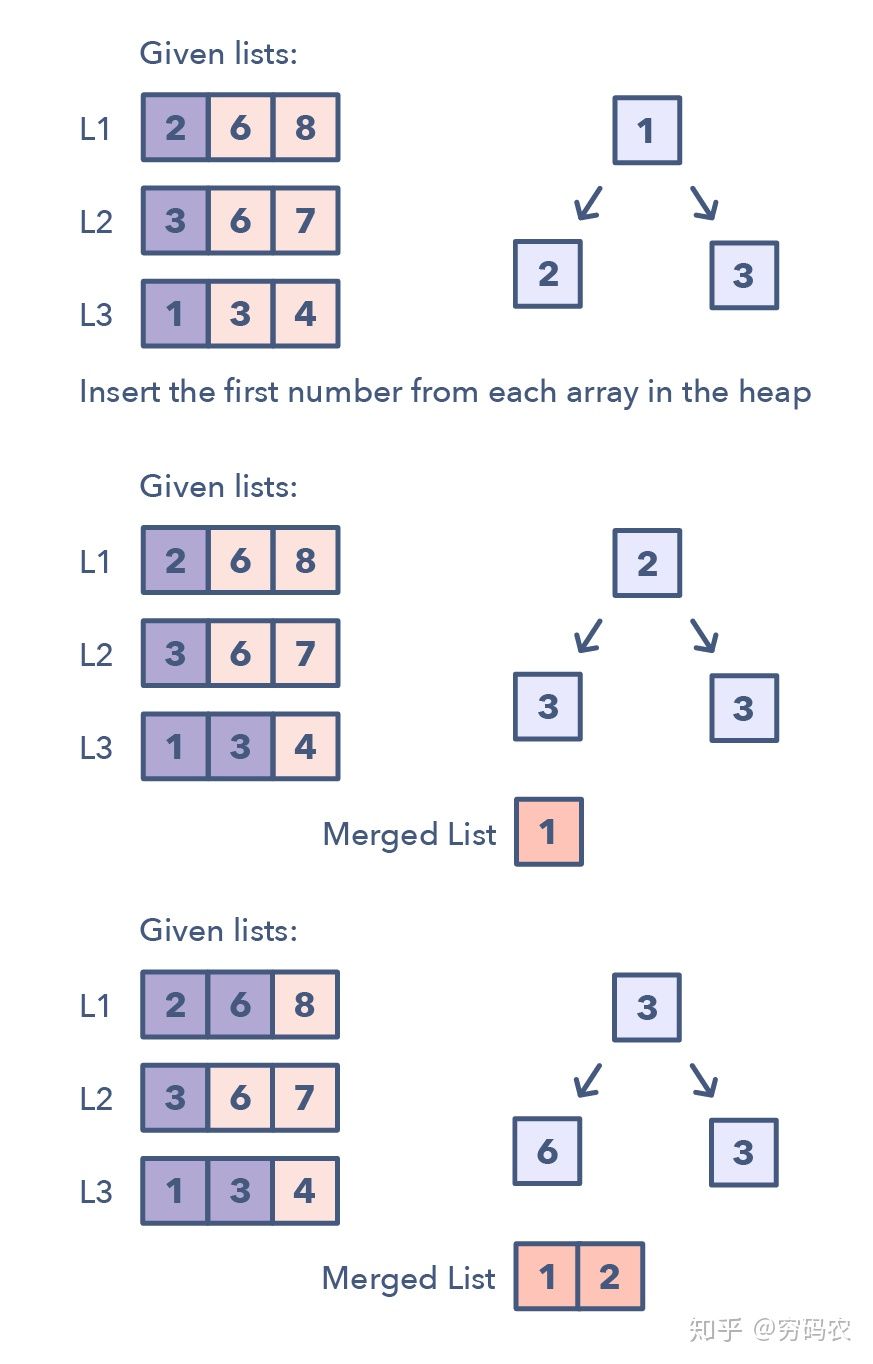
- merge K linked list
Topological sort
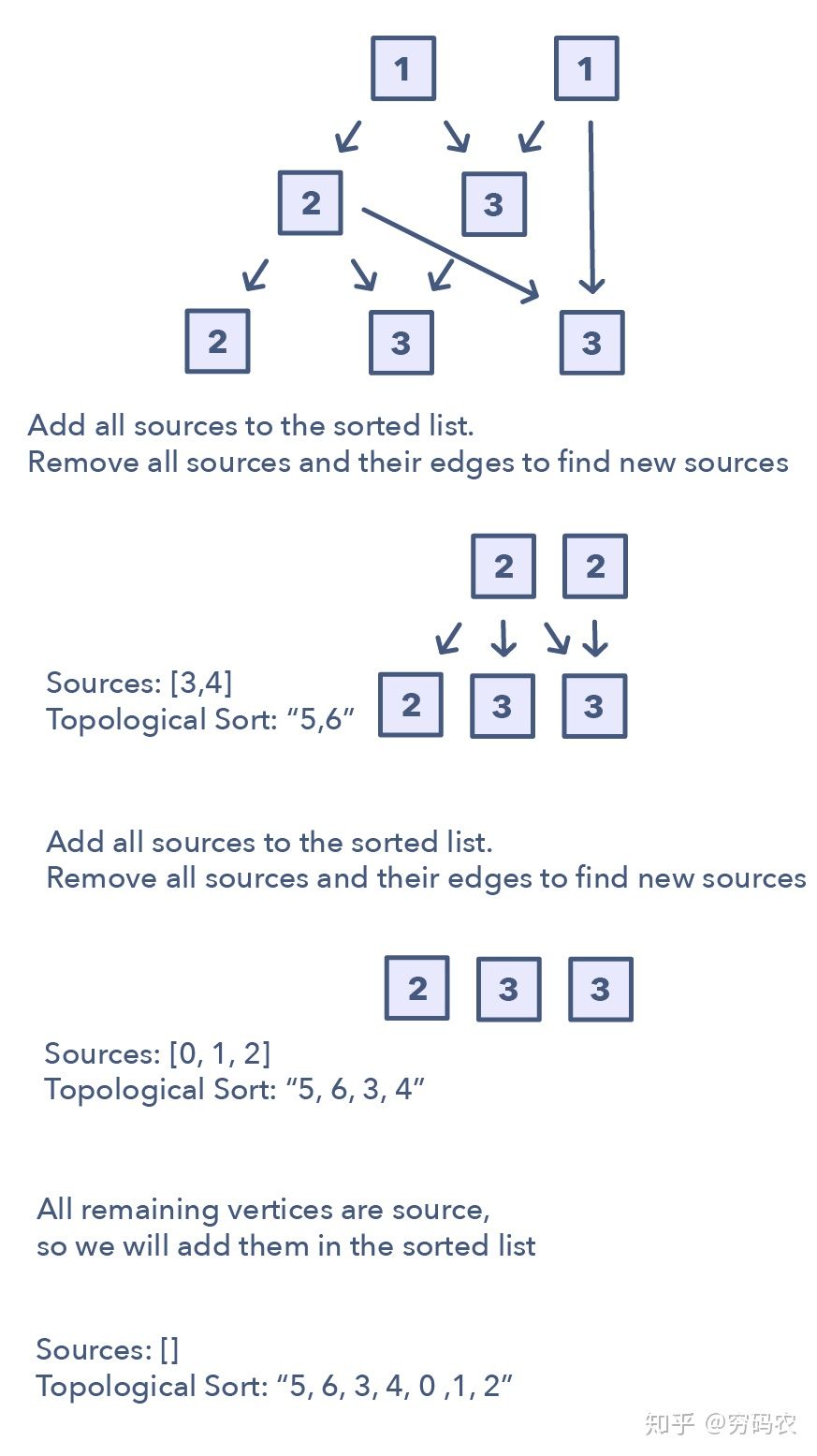 deal with graphs that have no directed cycles, or update all objects in a sorted order, or object following a particular order
deal with graphs that have no directed cycles, or update all objects in a sorted order, or object following a particular order
- Task scheduling
- Minimum height of a tree
string manipulation
add string
Given two non-negative integers num1 and num2 represented as string, return the sum of num1 and num2.
def solution(num1, num2):
n1, n2 = 0, 0
m1, m2 = 10**(len(num1)-1), 10**(len(num2)-1)
for i in num1:
n1 += (ord(i) - ord("0")) * m1
m1 = m1//10
for i in num2:
n2 += (ord(i) - ord("0")) * m2
m2 = m2//10
return str(n1 + n2)
print(solution(num1, num2))
First Unique Character
Given a string, find the first non-repeating character in it and return its index.
import collections
def solution(s):
# build hash map : character and how often it appears
count = collections.Counter(s) # <-- gives back a dictionary with words occurrence count
#Counter({'l': 1, 'e': 3, 't': 1, 'c': 1, 'o': 1, 'd': 1})
# find the index
for idx, ch in enumerate(s):
if count[ch] == 1:
return idx
return -1
manipulate arrays
monotonic array
Given an array of integers, determine whether the array is monotonic or not.
A = [6, 5, 4, 4]
B = [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2]
C = [1,1,2,3,7]
def solution(nums):
return (all(nums[i] <= nums[i + 1] for i in range(len(nums) - 1)) or
all(nums[i] >= nums[i + 1] for i in range(len(nums) - 1)))
print(solution(A))
print(solution(B))
print(solution(C))
Move Zeroes
#Given an array nums, write a function to move all zeroes to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
array1 = [0,1,0,3,12]
array2 = [1,7,0,0,8,0,10,12,0,4]
def solution(nums):
for i in nums:
if 0 in nums:
nums.remove(0)
nums.append(0)
return nums
solution(array1)
solution(array2)
Matched & Mismatched Words
#Given two sentences, return an array that has the words that appear in one sentence and not the other and an array with the words in common.
sentence1 = 'We are really pleased to meet you in our city'
sentence2 = 'The city was hit by a really heavy storm'
def solution(sentence1, sentence2):
set1 = set(sentence1.split())
set2 = set(sentence2.split())
return sorted(list(set1^set2)), sorted(list(set1&set2)) # ^ A.symmetric_difference(B), & A.intersection(B)
print(solution(sentence1, sentence2))