embeding
GloVe average embedding
unsupervised learning algorithm for obtaining vector representations for words. There is pretrained embeding in standford NLP website, which is called glove.6B.zip
# loading glove data file
# URL to donwload the GloVe embedding: https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/
D = 50
glove_data_file = f'data/glove.6B.{D}d.txt'
words = pd.read_csv(glove_data_file, sep=" ", index_col=0, header=None, quoting=csv.QUOTE_NONE)
# creating a dictionary for accessing words quickly
words_dict = {word: embed for word, embed in zip(words.index, words.values.tolist())}
print(f'Loaded {len(words_dict.keys())} words from the GloVe file')
def vec(w, D=50):
"""
Converts a word to an embedding vector
"""
try:
return np.array(words_dict[w])
# if the word is not in our vocabulary, we return zeros
except:
return np.zeros(D)
def average_embedding(sentence, D=50):
"""
Computes the average embedding of a sentence
"""
total_embeddings = np.zeros(D)
num_words = len(sentence.split())
# a sanity check
if num_words == 0:
return total_embeddings
# getting the embedding for each word
for word in sentence.split():
emb = vec(word)
total_embeddings += emb
# averaging the embeddings
avg_embeddings = total_embeddings/num_words
# so that we are not dividing by zero
if np.linalg.norm(avg_embeddings) > 1e-10:
return avg_embeddings/np.linalg.norm(avg_embeddings)
else:
return avg_embeddings
def preprocessing(sentence):
"""
Preprocessing. Removes punctuation and stop words
"""
# removing extra whitespace and making the sentence lower case
sentence = sentence.lower().strip()
# removing punctuation
bad_chars = '-.?;,!@#$%^&*()+/{}[]\\":\'“’'
for char in bad_chars:
sentence = sentence.replace(char, ' ').strip()
all_words = sentence.split()
# removing stop words
filtered_sentence = [w for w in all_words if not w in stopwords]
return ' '.join(filtered_sentence) ### Universal Sentence Encoder (USE) Embedding 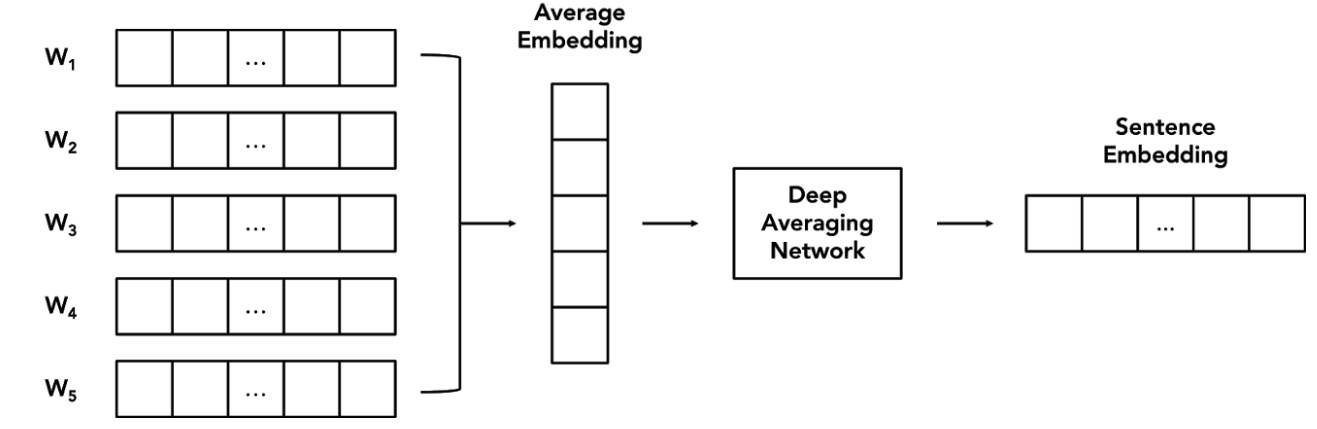 it is able to capture both syntactic and semantic information solely from the average word embeddings, and there is zero preprocessing required on the user end
# import dependencies
# tensorflow>=2.0.0
# tensorflow_hub>=0.6.0
import tensorflow as tf
print(f'Tensorflow version {tf.__version__}') # should be 2.0.0 or greater
import tensorflow_hub as hub
# load pretrained USE
try:
# if hub.load() fails, download is available directly from url
use_encoder = hub.load("https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder/4")
except:
# download model from website
# load model from directory if hub load fails on link
use_encoder = hub.load('USE/')
start_time = time.time()
# saving the use embeddings for all the image captions to a numpy array
use_img_embedding = np.zeros((len(image_df),512))
for i, text in enumerate(image_df.caption.values):
if i % 100000 == 0 and i > 0:
print(f'{i} out of {len(image_df.caption.values)} done in {time.time() - start_time:.2f}s')
emb = use_encoder([text])
use_img_embedding[i] = emb
print(f'{i} out of {len(image_df.caption.values)} done')
# normalize embeddings
use_img_embedding_normalized = use_img_embedding/np.linalg.norm(use_img_embedding,axis=1).reshape(-1,1)
library
nltk(Natural Language Toolkit)
Installation
!pip install nltk
nltk.download()
Usage
Tokenization
from nltk import word_tokenize, sent_tokenize
sent = "I will walk 500 miles and I would walk 500 more, just to be the man who walks a thousand miles to fall down at your door!"
print(word_tokenize(sent))
print(sent_tokenize(sent))
Stop-words
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = stopwords.words('english')
token = word_tokenize(sent)
cleaned_token = []
for word in token:
if word not in stop_words:
cleaned_token.append(word)
print("This is the unclean version:", token)
print("This is the cleaned version:", cleaned_token)
Stemming
There are other stemmers like SnowballStemmer and LancasterStemmer but PorterStemmer is sort of the simplest one
from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer
stemmer = PorterStemmer()
words = ['play', 'playing', 'plays', 'played',
'playfullness', 'playful']
stemmed = [stemmer.stem(word) for word in words]
print(stemmed)
Tagging Parts of Speech (pos)
takes in a list of tokenized words, and tags each of them with a corresponding Parts of Speech identifier into tuples
from nltk import pos_tag
token = word_tokenize(sent) + word_tokenize(sent2)
tagged = pos_tag(cleaned_token)
print(tagged)
StanfordNLP
CoreNLP is a library supporting all NLP operations like stemming, lementing, tokenization, finding parts of speech, sentiment analysis. StanfordNLP is a python wrapper for CoreNLP.
Installation
pip install stanfordnlp
Usage example
import stanfordnlp as st
st.download(‘en’)
pipe = stanfordnlp.Pipeline()
text = pipe("test text")
Owl
Owl is word similarity API, it uses the largest word2vec English model created by spaCy (en-core-web-lg) for the general context and uses one of the word2vec models created at Stanford University (glove-wiki-gigaword-300) for the news context.
the results are well-separated to the models, makers, and general subgroups
Usage
import requests
url = "https://word-similarity.p.rapidapi.com/news/10/apple"
headers = {
'x-rapidapi-host': "word-similarity.p.rapidapi.com",
'x-rapidapi-key': *** YOUR API KEY ***
}
response = requests.request("GET", url, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
TextBlob
it is text-processing interface, which is similar to python string
#install
pip install -U textblob
python -m textblob.download_corpora
usage
after wrapping string with TextBlob, you can easily access different text processing methods
from textblob import TextBlob
blob = TextBlob(text)
Word Tokenization
splitting word with direct call of blob.words, return value is WordList type, which can be used as a Python list
blob.words
Noun Phrase Extraction
extract noun phrase from text with blob.noun_phrases
blob.noun_phrases
Sentiment Analysis
do sentiment analysis with blob.sentiment, return value is a sentiment object.
Polarity is in the range of (-1,1); if polarity is <0, the sentence is more negative than positive and vice verse.
Subjectivity is in the range of (0,1); if subjectivity <0.5, the sentence is more subjective than objective and vice versa
blob.sentiment
Lemmatization
wrap the word inside Word object
for word in blob.words:
w = Word(word.lower())
print(w.lemmatize('v'))
Spelling Correction
#correct a sentence
blob.correct()
#correct word
from textblob import Word
Word('larnin').spellcheck()
Word Frequencies
from newspaper import Article
url = 'https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-learn-data-science-when-life-does-not-give-you-a-break-a26a6ea328fd'
article = Article(url)
article.download()
article.parse()
text = article.text
blob = TextBlob(text)
blob.word_counts['i']
#visualize frequency plot
import plotly.express as px
import pandas as pd
frequency = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(blob.word_counts, orient='index', columns=['count'])
px.bar(frequency.sort_values(by='count', ascending=False)[:30])
tricks and tips
cleaning text data
# # In case of import errors
# ! pip install nltk
# ! pip install textblob
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import re
import nltk
import string
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
# download all-nltk
nltk.download()
df = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
stop_words = stopwords.words("english")
#Lemmatization is a process of turning the words into their base or dictionary form
wordnet = WordNetLemmatizer()
def text_preproc(x):
#lowercase the text
x = x.lower()
#remove stop words
x = ' '.join([word for word in x.split(' ') if word not in stop_words])
#remove unicode characters
x = x.encode('ascii', 'ignore').decode()
#remove url
x = re.sub(r'https*\S+', ' ', x)
#remove mentions
x = re.sub(r'@\S+', ' ', x)
#Remove Hashtags
x = re.sub(r'#\S+', ' ', x)
#Remove ticks and the next character
x = re.sub(r'\'\w+', '', x)
#Remove punctuations
x = re.sub('[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuation), ' ', x)
#Remove numbers
x = re.sub(r'\w*\d+\w*', '', x)
#Replace the over spaces
x = re.sub(r'\s{2,}', ' ', x)
return x
df['clean_text'] = df.text.apply(text_preproc)
Balance the imbalanced data with SMOTE
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
from imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler
from imblearn.pipeline import Pipeline # define pipeline
over = SMOTE(sampling_strategy=0.5)
under = RandomUnderSampler(sampling_strategy=0.8)
steps = [('o', over), ('u', under)]
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=steps)# transform the dataset
X, y = pipeline.fit_resample(X, labels['label'])# One-hot encoding of labels
from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categorical
y = to_categorical(y)