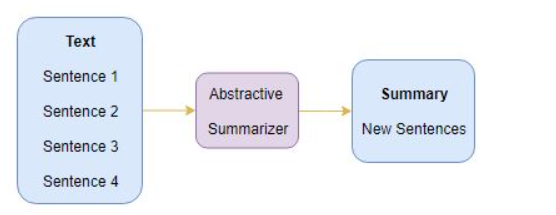
There are two approaches for text summarization:
-
abstractive summarization generate new sentences from the original text
-
extractive summarization
identify the important sentences or phrases from the original text and extract only those from the text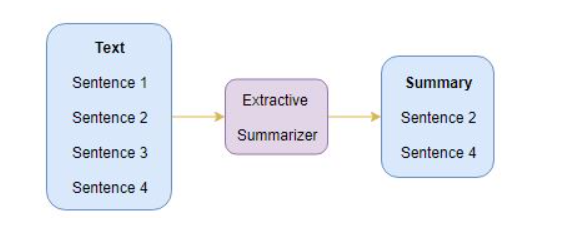
extractive summarization
TextRank
an extractive and unsupervised text summarization technique
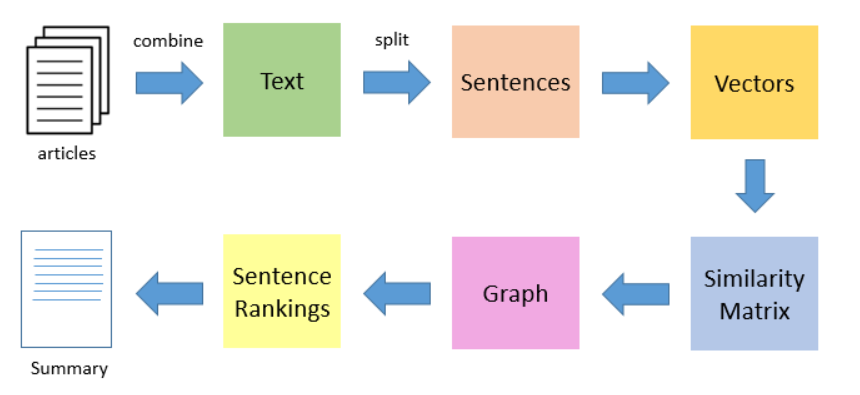
example
single-domain-multiple-documents summarization task example
#reference https://github.com/prateekjoshi565/textrank_text_summarization
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import nltk
nltk.download('punkt') # one time execution
import re
df = pd.read_csv("tennis_articles_v4.csv")
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
sentences = []
for s in df['article_text']:
sentences.append(sent_tokenize(s))
sentences = [y for x in sentences for y in x] # flatten list
#Download GloVe Word Embeddings
!wget http://nlp.stanford.edu/data/glove.6B.zip
!unzip glove*.zip
# Extract word vectors
word_embeddings = {}
f = open('glove.6B.100d.txt', encoding='utf-8')
for line in f:
values = line.split()
word = values[0]
coefs = np.asarray(values[1:], dtype='float32')
word_embeddings[word] = coefs
f.close()
#Text cleaning
# remove punctuations, numbers and special characters
clean_sentences = pd.Series(sentences).str.replace("[^a-zA-Z]", " ")
# make alphabets lowercase
clean_sentences = [s.lower() for s in clean_sentences]
#remove stop words
nltk.download('stopwords')
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = stopwords.words('english')
def remove_stopwords(sen):
sen_new = " ".join([i for i in sen if i not in stop_words])
return sen_new
# remove stopwords from the sentences
clean_sentences = [remove_stopwords(r.split()) for r in clean_sentences]
# Extract word vectors
word_embeddings = {}
f = open('glove.6B.100d.txt', encoding='utf-8')
for line in f:
values = line.split()
word = values[0]
coefs = np.asarray(values[1:], dtype='float32')
word_embeddings[word] = coefs
f.close()
sentence_vectors = []
for i in clean_sentences:
if len(i) != 0:
v = sum([word_embeddings.get(w, np.zeros((100,))) for w in i.split()])/(len(i.split())+0.001)
else:
v = np.zeros((100,))
sentence_vectors.append(v)
# similarity matrix
sim_mat = np.zeros([len(sentences), len(sentences)])
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
for i in range(len(sentences)):
for j in range(len(sentences)):
if i != j:
sim_mat[i][j] = cosine_similarity(sentence_vectors[i].reshape(1,100),sentence_vectors[j].reshape(1,100))[0,0]
#Applying PageRank Algorithm
import networkx as nx
nx_graph = nx.from_numpy_array(sim_mat)
scores = nx.pagerank(nx_graph)
#Summary Extraction
ranked_sentences = sorted(((scores[i],s) for i,s in enumerate(sentences)), reverse=True)
# Extract top 10 sentences as the summary
for i in range(10):
print(ranked_sentences[i][1])
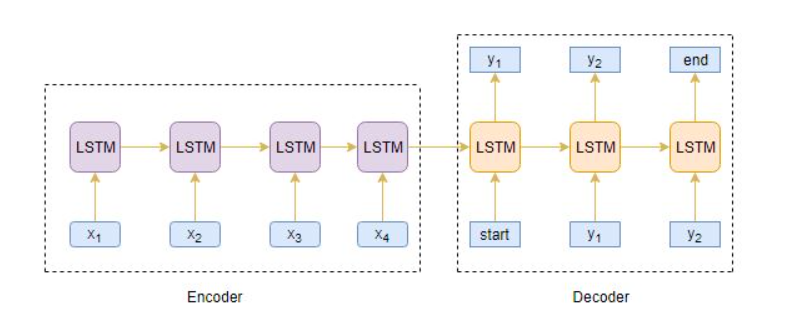
Abstractive Summarization
Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) Modeling
text summarization can be seen as a Many-to-Many Seq2Seq problem
 besides keras library there is one seq2seq open source model pegasus availab: https://github.com/google-research/pegasus
besides keras library there is one seq2seq open source model pegasus availab: https://github.com/google-research/pegasus
example
reference: https://github.com/aravindpai/How-to-build-own-text-summarizer-using-deep-learning/blob/master/How_to_build_own_text_summarizer_using_deep_learning.ipynb
1) load library
#attension layer is this third-party implementation https://github.com/thushv89/attention_keras/tree/master/src/layers
from attention import AttentionLayer
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, LSTM, Embedding, Dense, Concatenate, TimeDistributed, Bidirectional
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
import warnings
pd.set_option("display.max_colwidth", 200)
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
2) read data
data=pd.read_csv("../input/amazon-fine-food-reviews/Reviews.csv",nrows=100000)
#clean data
data.drop_duplicates(subset=['Text'],inplace=True) #dropping duplicates
data.dropna(axis=0,inplace=True) #dropping na
contraction_mapping = {"ain't": "is not", "aren't": "are not","can't": "cannot", "'cause": "because", "could've": "could have", "couldn't": "could not",
"didn't": "did not", "doesn't": "does not", "don't": "do not", "hadn't": "had not", "hasn't": "has not", "haven't": "have not",
"he'd": "he would","he'll": "he will", "he's": "he is", "how'd": "how did", "how'd'y": "how do you", "how'll": "how will", "how's": "how is",
"I'd": "I would", "I'd've": "I would have", "I'll": "I will", "I'll've": "I will have","I'm": "I am", "I've": "I have", "i'd": "i would",
"i'd've": "i would have", "i'll": "i will", "i'll've": "i will have","i'm": "i am", "i've": "i have", "isn't": "is not", "it'd": "it would",
"it'd've": "it would have", "it'll": "it will", "it'll've": "it will have","it's": "it is", "let's": "let us", "ma'am": "madam",
"mayn't": "may not", "might've": "might have","mightn't": "might not","mightn't've": "might not have", "must've": "must have",
"mustn't": "must not", "mustn't've": "must not have", "needn't": "need not", "needn't've": "need not have","o'clock": "of the clock",
"oughtn't": "ought not", "oughtn't've": "ought not have", "shan't": "shall not", "sha'n't": "shall not", "shan't've": "shall not have",
"she'd": "she would", "she'd've": "she would have", "she'll": "she will", "she'll've": "she will have", "she's": "she is",
"should've": "should have", "shouldn't": "should not", "shouldn't've": "should not have", "so've": "so have","so's": "so as",
"this's": "this is","that'd": "that would", "that'd've": "that would have", "that's": "that is", "there'd": "there would",
"there'd've": "there would have", "there's": "there is", "here's": "here is","they'd": "they would", "they'd've": "they would have",
"they'll": "they will", "they'll've": "they will have", "they're": "they are", "they've": "they have", "to've": "to have",
"wasn't": "was not", "we'd": "we would", "we'd've": "we would have", "we'll": "we will", "we'll've": "we will have", "we're": "we are",
"we've": "we have", "weren't": "were not", "what'll": "what will", "what'll've": "what will have", "what're": "what are",
"what's": "what is", "what've": "what have", "when's": "when is", "when've": "when have", "where'd": "where did", "where's": "where is",
"where've": "where have", "who'll": "who will", "who'll've": "who will have", "who's": "who is", "who've": "who have",
"why's": "why is", "why've": "why have", "will've": "will have", "won't": "will not", "won't've": "will not have",
"would've": "would have", "wouldn't": "would not", "wouldn't've": "would not have", "y'all": "you all",
"y'all'd": "you all would","y'all'd've": "you all would have","y'all're": "you all are","y'all've": "you all have",
"you'd": "you would", "you'd've": "you would have", "you'll": "you will", "you'll've": "you will have",
"you're": "you are", "you've": "you have"}
3) clean data
#clean reviews
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
def text_cleaner(text):
newString = text.lower()
newString = BeautifulSoup(newString, "lxml").text
newString = re.sub(r'\([^)]*\)', '', newString)
newString = re.sub('"','', newString)
newString = ' '.join([contraction_mapping[t] if t in contraction_mapping else t for t in newString.split(" ")])
newString = re.sub(r"'s\b","",newString)
newString = re.sub("[^a-zA-Z]", " ", newString)
tokens = [w for w in newString.split() if not w in stop_words]
long_words=[]
for i in tokens:
if len(i)>=3: #removing short word
long_words.append(i)
return (" ".join(long_words)).strip()
cleaned_text = []
for t in data['Text']:
cleaned_text.append(text_cleaner(t))
#clean summary
def summary_cleaner(text):
newString = re.sub('"','', text)
newString = ' '.join([contraction_mapping[t] if t in contraction_mapping else t for t in newString.split(" ")])
newString = re.sub(r"'s\b","",newString)
newString = re.sub("[^a-zA-Z]", " ", newString)
newString = newString.lower()
tokens=newString.split()
newString=''
for i in tokens:
if len(i)>1:
newString=newString+i+' '
return newString
#Call the above function
cleaned_summary = []
for t in data['Summary']:
cleaned_summary.append(summary_cleaner(t))
data['cleaned_text']=cleaned_text
data['cleaned_summary']=cleaned_summary
data['cleaned_summary'].replace('', np.nan, inplace=True)
data.dropna(axis=0,inplace=True)
#add start/stop token
data['cleaned_summary'] = data['cleaned_summary'].apply(lambda x : '_START_ '+ x + ' _END_')
4)get distribution of the data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
text_word_count = []
summary_word_count = []
# populate the lists with sentence lengths
for i in data['cleaned_text']:
text_word_count.append(len(i.split()))
for i in data['cleaned_summary']:
summary_word_count.append(len(i.split()))
length_df = pd.DataFrame({'text':text_word_count, 'summary':summary_word_count})
length_df.hist(bins = 30)
plt.show()
#set parameter according to the distribution
max_len_text=80
max_len_summary=10
#split data
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_tr,x_val,y_tr,y_val=train_test_split(data['cleaned_text'],data['cleaned_summary'],test_size=0.1,random_state=0,shuffle=True)
5) Preparing the Tokenizer
#text tokenizer
#prepare a tokenizer for reviews on training data
x_tokenizer = Tokenizer()
x_tokenizer.fit_on_texts(list(x_tr))
#convert text sequences into integer sequences
x_tr = x_tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(x_tr)
x_val = x_tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(x_val)
#padding zero upto maximum length
x_tr = pad_sequences(x_tr, maxlen=max_len_text, padding='post')
x_val = pad_sequences(x_val, maxlen=max_len_text, padding='post')
x_voc_size = len(x_tokenizer.word_index) +1
#summary tokenizer
#preparing a tokenizer for summary on training data
y_tokenizer = Tokenizer()
y_tokenizer.fit_on_texts(list(y_tr))
#convert summary sequences into integer sequences
y_tr = y_tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(y_tr)
y_val = y_tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(y_val)
#padding zero upto maximum length
y_tr = pad_sequences(y_tr, maxlen=max_len_summary, padding='post')
y_val = pad_sequences(y_val, maxlen=max_len_summary, padding='post')
y_voc_size = len(y_tokenizer.word_index) +1
6) model building
from keras import backend as K
K.clear_session()
latent_dim = 500
# Encoder
encoder_inputs = Input(shape=(max_len_text,))
enc_emb = Embedding(x_voc_size, latent_dim,trainable=True)(encoder_inputs)
#LSTM 1
encoder_lstm1 = LSTM(latent_dim,return_sequences=True,return_state=True)
encoder_output1, state_h1, state_c1 = encoder_lstm1(enc_emb)
#LSTM 2
encoder_lstm2 = LSTM(latent_dim,return_sequences=True,return_state=True)
encoder_output2, state_h2, state_c2 = encoder_lstm2(encoder_output1)
#LSTM 3
encoder_lstm3=LSTM(latent_dim, return_state=True, return_sequences=True)
encoder_outputs, state_h, state_c= encoder_lstm3(encoder_output2)
# Set up the decoder.
decoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None,))
dec_emb_layer = Embedding(y_voc_size, latent_dim,trainable=True)
dec_emb = dec_emb_layer(decoder_inputs)
#LSTM using encoder_states as initial state
decoder_lstm = LSTM(latent_dim, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
decoder_outputs,decoder_fwd_state, decoder_back_state = decoder_lstm(dec_emb,initial_state=[state_h, state_c])
#Attention Layer
Attention layer attn_layer = AttentionLayer(name='attention_layer')
attn_out, attn_states = attn_layer([encoder_outputs, decoder_outputs])
# Concat attention output and decoder LSTM output
decoder_concat_input = Concatenate(axis=-1, name='concat_layer')([decoder_outputs, attn_out])
#Dense layer
decoder_dense = TimeDistributed(Dense(y_voc_size, activation='softmax'))
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_concat_input)
# Define the model
model = Model([encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs], decoder_outputs)
model.summary()
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy')
es = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', mode='min', verbose=1)
history=model.fit([x_tr,y_tr[:,:-1]], y_tr.reshape(y_tr.shape[0],y_tr.shape[1], 1)[:,1:] ,epochs=50,callbacks=[es],batch_size=512, validation_data=([x_val,y_val[:,:-1]], y_val.reshape(y_val.shape[0],y_val.shape[1], 1)[:,1:]))
7) Understanding the Diagnostic plot
from matplotlib import pyplot
pyplot.plot(history.history['loss'], label='train')
pyplot.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label='test')
pyplot.legend() pyplot.show()
reverse_target_word_index=y_tokenizer.index_word
reverse_source_word_index=x_tokenizer.index_word
target_word_index=y_tokenizer.word_index
8) inference
def decode_sequence(input_seq):
# Encode the input as state vectors.
e_out, e_h, e_c = encoder_model.predict(input_seq)
# Generate empty target sequence of length 1.
target_seq = np.zeros((1,1))
# Chose the 'start' word as the first word of the target sequence
target_seq[0, 0] = target_word_index['start']
stop_condition = False
decoded_sentence = ''
while not stop_condition:
output_tokens, h, c = decoder_model.predict([target_seq] + [e_out, e_h, e_c])
# Sample a token
sampled_token_index = np.argmax(output_tokens[0, -1, :])
sampled_token = reverse_target_word_index[sampled_token_index]
if(sampled_token!='end'):
decoded_sentence += ' '+sampled_token
# Exit condition: either hit max length or find stop word.
if (sampled_token == 'end' or len(decoded_sentence.split()) >= (max_len_summary-1)):
stop_condition = True
# Update the target sequence (of length 1).
target_seq = np.zeros((1,1))
target_seq[0, 0] = sampled_token_index
# Update internal states
e_h, e_c = h, c
return decoded_sentence
def seq2summary(input_seq):
newString=''
for i in input_seq:
if((i!=0 and i!=target_word_index['start']) and i!=target_word_index['end']):
newString=newString+reverse_target_word_index[i]+' '
return newString
def seq2text(input_seq):
newString=''
for i in input_seq:
if(i!=0):
newString=newString+reverse_source_word_index[i]+' '
return newString
for i in range(len(x_val)):
print("Review:",seq2text(x_val[i]))
print("Original summary:",seq2summary(y_val[i]))
print("Predicted summary:",decode_sequence(x_val[i].reshape(1,max_len_text)))
print("\n")
Tips
KEP - Keyphrase Extraction Package
a Python package that enables to extract keyphrases from documents
docker pull liaad/kep
docker run -p 9999:8888 --user root liaad/kep
http://<DOCKER-MACHINE-IP>:8888