Gradient Descent
Stochastic Gradient Descent
Adaptive Learning Rate Method
non-gradient Descent
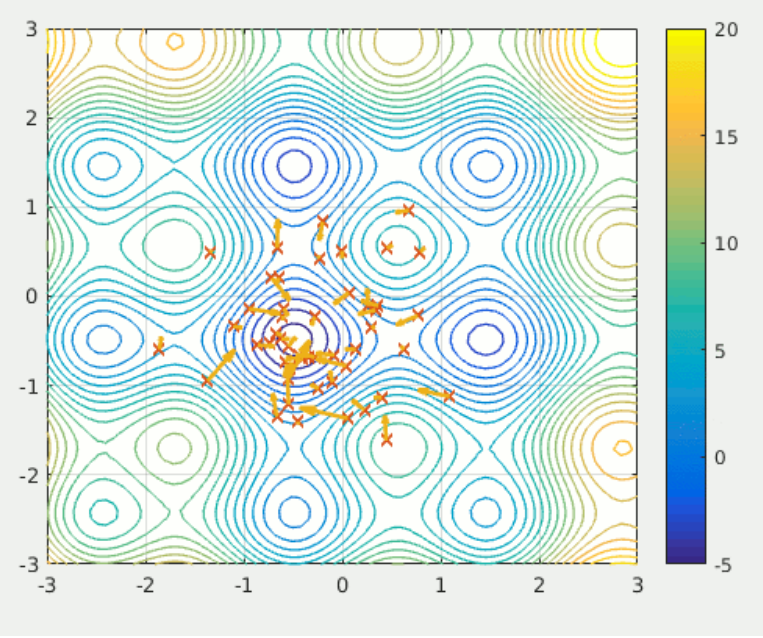
Particle Swarm Optimization
a population-based method that defines a set of ‘particles’ that explore the search space, attempting to find a minimum.
- does not require the optimization problem to be differentiable
- makes little to no assumptions about the problem being optimized and can search very large spaces
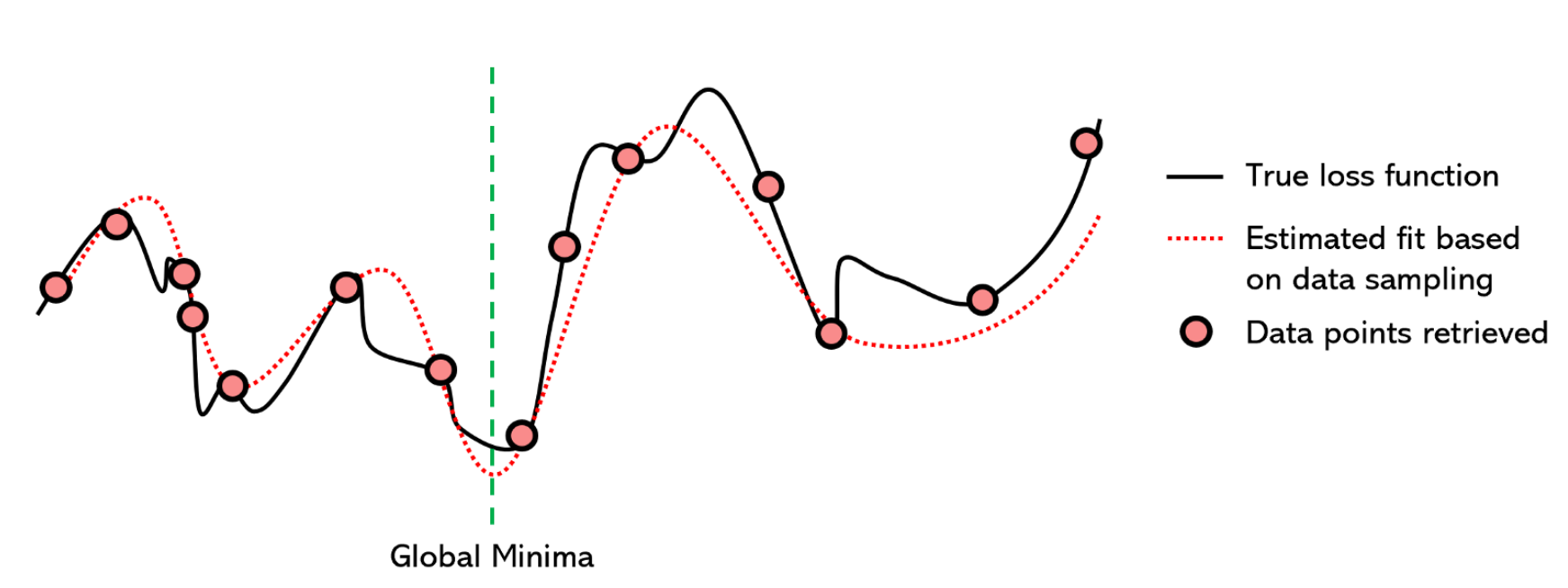
Surrogate optimization
a method of optimization that attempts to model the loss function with another well-established function to find the minima.
- a non-iterative method
- can handle large data and non-differentiable optimization problems
- almost always faster than gradient descent methods, but often at the cost of accuracy
Simulated Annealing
The temperature is set at some initial positive value and progressively approaches zero.
At each time step, the algorithm randomly chooses a solution close to the current one, measures its quality, and moves to it depending on the current temperature (probability of accepting better or worse solutions).
Ideally, by the time the temperature reaches zero, the algorithm has converged on a global minima solution.
- performs especially well in scenarios where an approximate solution is required in a short period of time,
tips
single objective optimization
you can find all single objective optimization function in python here: https://github.com/AxelThevenot/Python_Benchmark_Test_Optimization_Function_Single_Objective