automl can deploy thousands of models in production, with far less grunt work and hand-tuning, reducing turn-around-time drastically.
Auto-Sklearn
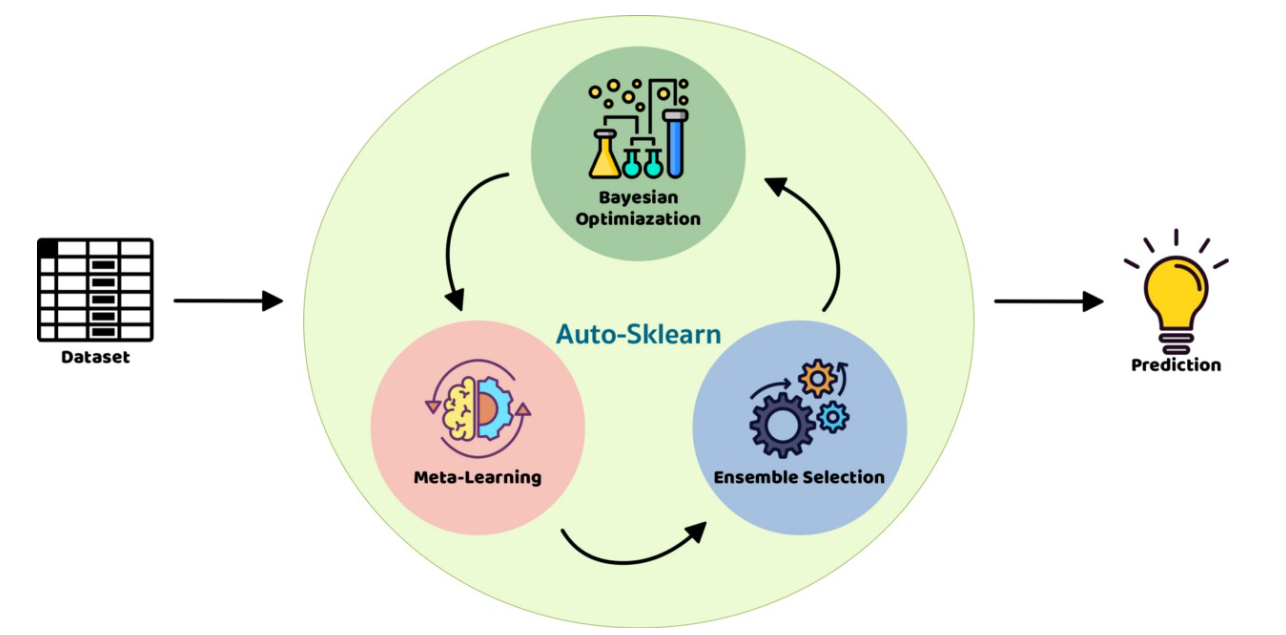 it implements Bayesian Optimization for searching of the optimal pipeline configuration as well as Ensemble Selection for the choosing of the right model. it is composed of 15 classifiers, 14 preprocessing methods, and 4 data preprocessing methods.
it implements Bayesian Optimization for searching of the optimal pipeline configuration as well as Ensemble Selection for the choosing of the right model. it is composed of 15 classifiers, 14 preprocessing methods, and 4 data preprocessing methods.
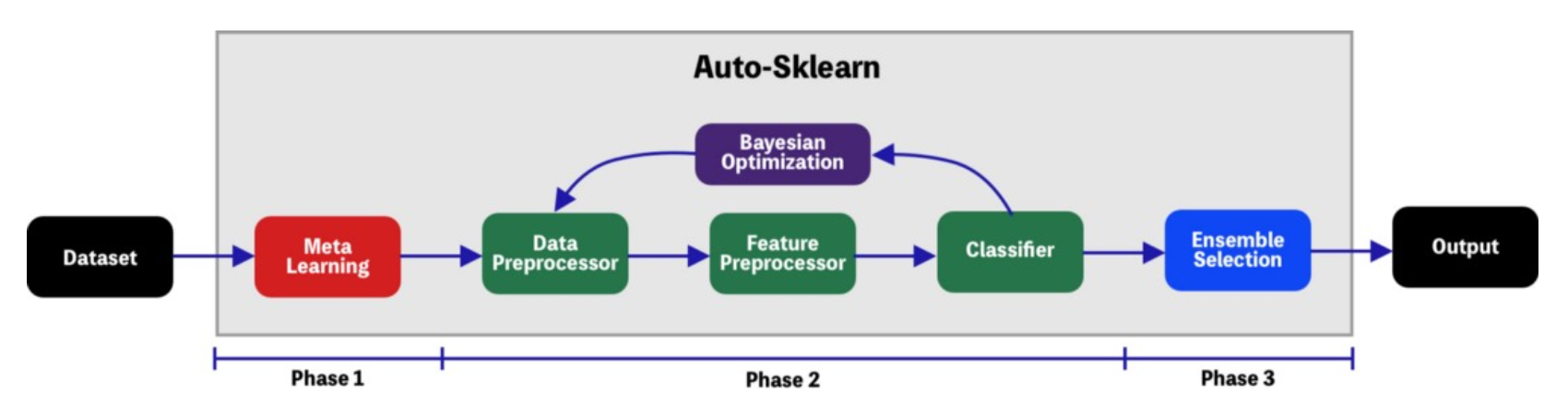
- meta-learning: reduce the space search by learning from models that performed well on similar datasets
- bayesian optimization: takes the space search created in the meta-learning step and creates bayesian models for finding the optimal pipeline configuration
- ensemble selection: a combi model that reuses the most accurate models found in the bayesian optimization step
```# For this basic implementation, we only need these modules from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from autosklearn.classification import AutoSklearnClassifier
Load the well-known Breast Cancer dataset
Split into train and test sets
x, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=23)
Auto-Sklearn Initialization
model = AutoSklearnClassifier()
Init training
model.fit(x_train, y_train) #check performance of the model $ model.score(x_train, y_train) 0.960093896713615 $ model.score(x_test, y_test) 0.965034965034965 $ print(model.sprint_statistics())
## tpot
tpot is an automated machine learning tool in python. the official user manual is here: http://epistasislab.github.io/tpot/api/
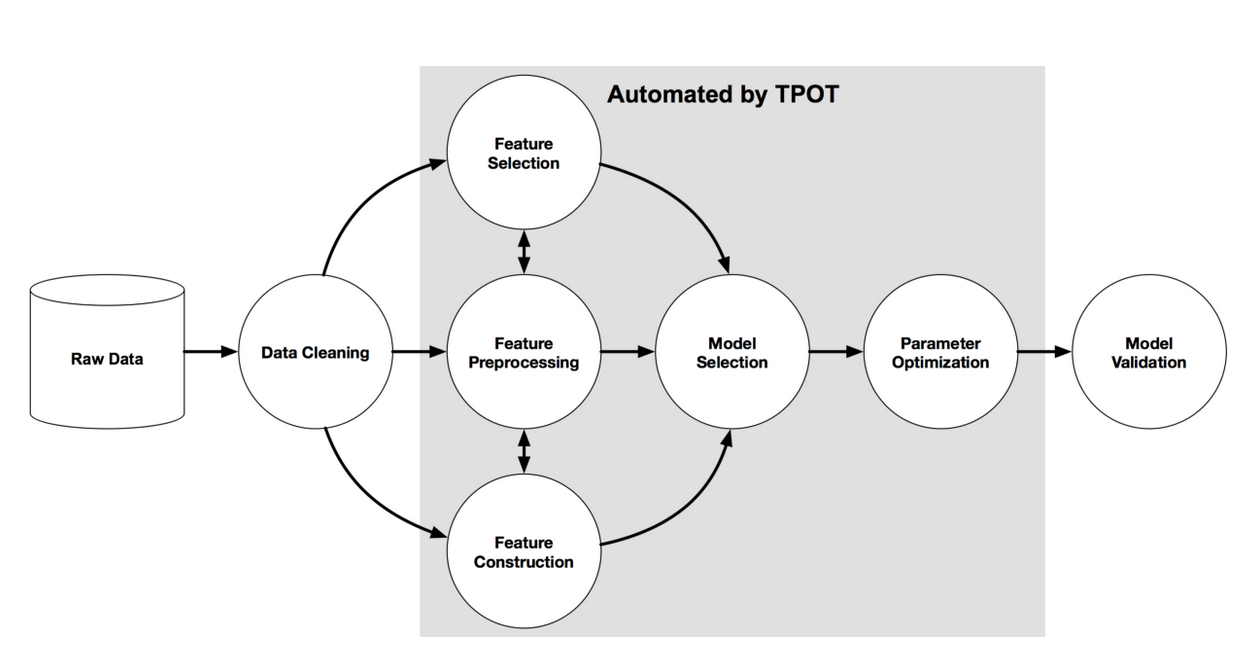
it isn’t designed for automating deep learning, but rather classical machine learning. it is built on the scikit learn library and follows the scikit learn API. Typical user cases are: regression and classification.
remember that: tpot does not have Reproducibility for the results!!
### usage
tpot = TPOTClassifier()
tpot.fit(X_train, y_train)
tpot.score(X_test, y_test)
#### example
1) MNIST
# import the usual stuff
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import os# import TPOT and sklearn stuff
from tpot import TPOTClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import sklearn.metrics# create train and test sets
digits = load_digits()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(digits.data, digits.target, train_size=0.75, test_size=0.25, random_state=34)
#total number of pipeline: POPULATION_SIZE + GENERATIONS x OFFSPRING_SIZE
#the accuracy is better with more number of pipeline
tpot = TPOTClassifier(verbosity=3,
scoring="balanced_accuracy",
random_state=23,
periodic_checkpoint_folder="tpot_mnst1.txt",
n_jobs=-1,
generations=10,
population_size=100)
# run three iterations and time them
for x in range(3):
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
tpot.fit(X_train, y_train)
elapsed = timeit.default_timer() - start_time
times.append(elapsed)
winning_pipes.append(tpot.fitted_pipeline_)
scores.append(tpot.score(X_test, y_test))
tpot.export('tpot_mnist_pipeline.py')
times = [time/60 for time in times]
print('Times:', times)
print('Scores:', scores)
print('Winning pipelines:', winning_pipes)
## FLAML
```#installation
pip install flaml
Usage
1) Classification
```from flaml importAutoML from sklearn.datasets import load_iris automl = AutoML automl_settings = { “time_budget”: 10, # in seconds “metric”: ‘accuracy’, “task”: ‘classification’ } X_train, y_train = load_iris(return_X_y= True)
Train with labeled input data
automl.fit(X_train=X_train, y_train=y_train, **automl_settings) print(automl.predict_proba(X_train).shape)
Export the best model
print(automl.model) print( ‘Best ML leaner:’, automl.best_estimator) print( ‘Best hyperparmeter config:’, automl.best_config) print( ‘Best accuracy on validation data: {0:.4g}’.format( 1-automl.best_loss)) print( ‘Training duration of best run: {0:.4g} s’.format(automl.best_config_train_time))
2) regression
```from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
automl = AutoML
automl_settings = {
"time_budget": 10, # in seconds
"metric": 'r2',
"task": 'regression'
}
X_train, y_train = load_boston(return_X_y= True)
# Train with labeled input data
automl.fit(X_train=X_train, y_train=y_train, **automl_settings)
# Predict
print(automl.predict(X_train).shape)
# Export the best model
print(automl.model)
print( 'Best ML leaner:', automl.best_estimator)
print( 'Best hyperparmeter config:', automl.best_config)
print( 'Best accuracy on validation data: {0:.4g}'.format( 1-automl.best_loss))
print( 'Training duration of best run: {0:.4g} s'.format(automl.best_config_train_time))
ray
installation
pip install ray
pip install alfred-py
usage
- tune hyperparameter
'''
this projects demonstrate
how to tune
hyper parameters on a model
'''
from ray.tune.schedulers import ASHAScheduler
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from ray import tune
from ray.tune.examples.mnist_pytorch import get_data_loaders
, train, test
import ray
import sys
from alfred.dl.torch.common import device
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
ray.init(redis_address=sys.argv[1])
class ConvNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ConvNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 3, kernel_size=3)
self.fc = nn.Linear(192, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 3))
x = x.view(-1, 192)
x = self.fc(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
def train_mnist(config):
model = ConvNet()
model.to(device)
train_loader, test_loader = get_data_loaders()
optimizer = optim.SGD(
model.parameters(), lr=config["lr"], momentum=config["momentum"])
for i in range(10):
train(model, optimizer, train_loader, device)
acc = test(model, test_loader, device)
# tune.track.log(mean_accuracy=acc)
tune.report(mean_accuracy=acc)
if i % 5 == 0:
# This saves the model to the trial directory
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./model.pth")
search_space = {
"lr": tune.choice([0.001, 0.01, 0.1]),
"momentum": tune.uniform
(0.1, 0.9)
}
analysis = tune.run(
train_mnist,
num_samples=30,
resources_per_trial={'gpu': 1},
scheduler=ASHAScheduler(metric="mean_accuracy",
mode="max", grace_period=1),
config=search_space)
- search in large network ``` 作者:金天 链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/461037620/answer/2339439801 来源:知乎 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
import detectron2 from detectron2.utils.logger import setup_logger setup_logger()
import detectron2.data.transforms as T
import some common detectron2 utilities
from detectron2 import model_zoo from detectron2.data import detection_utils as utils from detectron2.data import MetadataCatalog, DatasetCatalog, build_detection_train_loader, DatasetMapper, build_detection_test_loader from detectron2.engine import DefaultTrainer, DefaultPredictor from detectron2.config import get_cfg from detectron2.evaluation import COCOEvaluator, inference_on_dataset from detectron2.engine.hooks import HookBase from detectron2.data.datasets import register_coco_instances, load_coco_json from detectron2.utils.visualizer import Visualizer, ColorMode from detectron2.structures.boxes import BoxMode
import numpy as np import os, json, cv2, random
import PointRend project
from detectron2.projects import point_rend
import copy import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
from torchvision.transforms import functional as F import random import albumentations as A
Hyperparametertuning
import ray from functools ```