genetic algorithm
a population-based evolutionary algorithm, where a group of solutions works together to find the optimal parameters for a problem
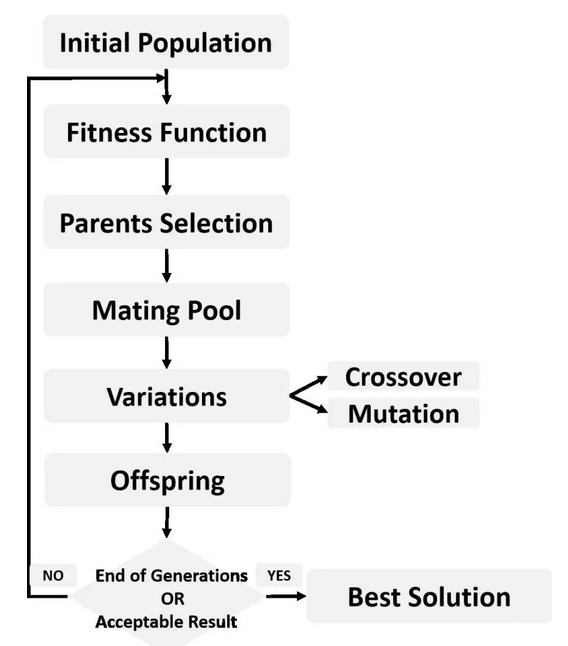 To produce the offspring, pairs of parents mate using the crossover operation, where a new solution is generated that carries genes from its parents. After crossover, mutation is applied to add some random changes over the solution. The evolution continues through a number of generations to reach the highest-quality solution
To produce the offspring, pairs of parents mate using the crossover operation, where a new solution is generated that carries genes from its parents. After crossover, mutation is applied to add some random changes over the solution. The evolution continues through a number of generations to reach the highest-quality solution
Random mutation
- Build the fitness function which is a regular Python function (maximization function).
- Create an instance of the pygad.GA class.
- Call the run() method.
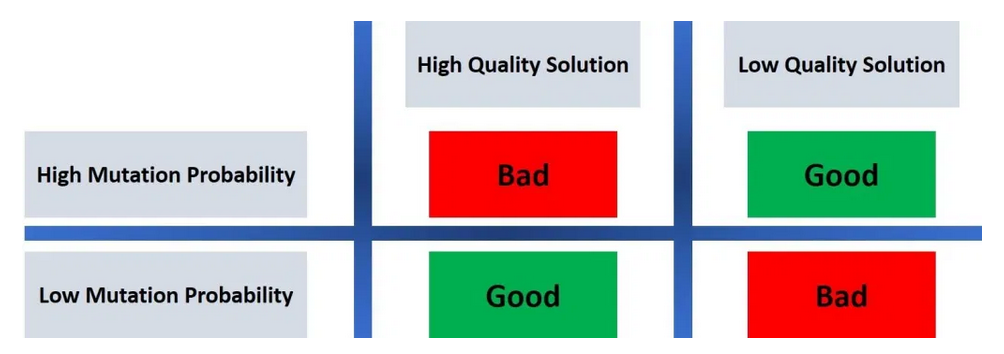
constant mutation probability
A small mutation probability is good for high-quality solutions, but bad for low-quality ones.
A high mutation probability is good for low-quality solutions, but bad for high-quality ones.
#install python3 pygad library
#pip install pygad
import pygad
import numpy
function_inputs = [4,-2,3.5,5]
desired_output = 44
def fitness_func(solution, solution_idx):
output = numpy.sum(solution*function_inputs)
fitness = 1.0 / (numpy.abs(output - desired_output) + 0.000001)
return fitness
ga_instance = pygad.GA(num_generations=100,
sol_per_pop=5,
num_genes=4,
num_parents_mating=2,
fitness_func=fitness_func,
mutation_type="random",
mutation_probability=0.6)
ga_instance.run()
ga_instance.plot_result()
adaptive mutation
#install pygrad higher than 2.10.0
#pip install pygad==2.10.*
import pygad
import numpy
function_inputs = [4,-2,3.5,5]
desired_output = 44
def fitness_func(solution, solution_idx):
output = numpy.sum(solution*function_inputs)
fitness = 1.0 / (numpy.abs(output - desired_output) + 0.000001)
return fitness
ga_instance = pygad.GA(num_generations=100,
sol_per_pop=5,
num_genes=4,
num_parents_mating=2,
fitness_func=fitness_func,
mutation_type="adaptive",
mutation_probability=[0.6, 0.2])
ga_instance.run()
ga_instance.plot_result()