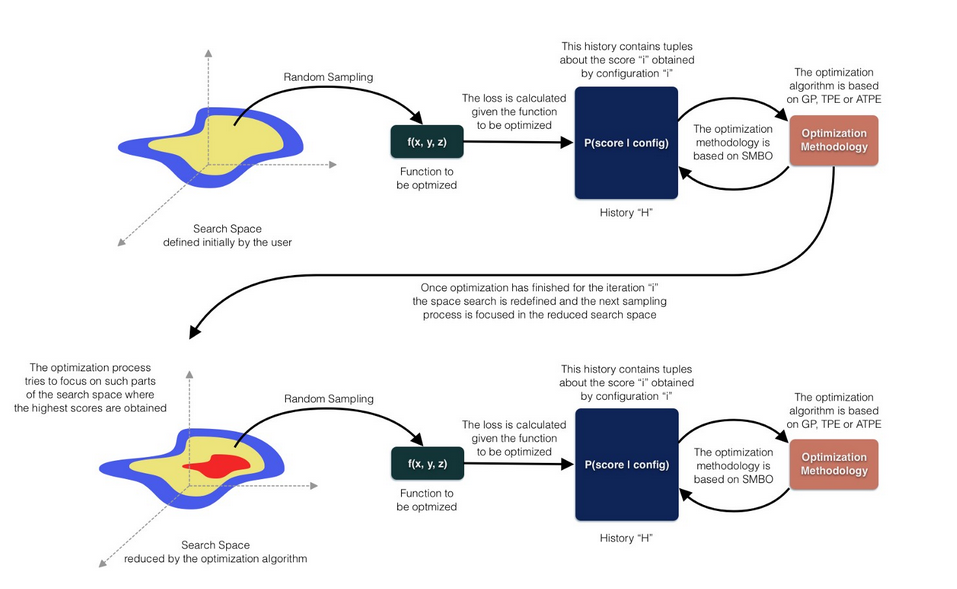
Hyperopt is a tool for finding the optimal hyperparameter based on a Bayesian Optimization and supported by the SMBO (Sequential Model-Based Global Optimization) methodology, such as Tree of Parzen Estimators (TPE), Adaptive Tree of Parzen Estimators (ATPE) and Gaussian Processes (GP).
hyperopt
HyperOpt was designed to optimize hyperparameters of one or several given functions under the paradigm of Bayesian optimization. HyperOpt requires 4 parameters for a basic implementation which are: the function to be optimized, the search space, the optimizer algorithm and the number of iterations. an example is like:
# fmin: class which will host optimization process
# tpe: the optimizer to be used (Tree of Parzen Estimator)
# hp: for defining the search space
from hyperopt import fmin, tpe, hp
# Function to be optimized
def f(x):
return x**2 + x + 1
# Search space definition
space = hp.uniform('x', -2, 2)
# Init the optimizer
# fn: function to be optimized
# space: search space
# algo: optimizer algorithm
# max_evals: number of iterations
best = fmin(
fn=f,
space=space,
algo=tpe.suggest,
max_evals=1000
)
print(f"Optimal value of x: {best}")
hyperopt-sklearn
HyperOpt-Sklearn’s objectives is optimizing different components of machine learning pipelines by addressing specifically the phases of data transformation, model selection and hyperparameter optimization using HyperOpt as the core and taking various components from the scikit-learn suite.
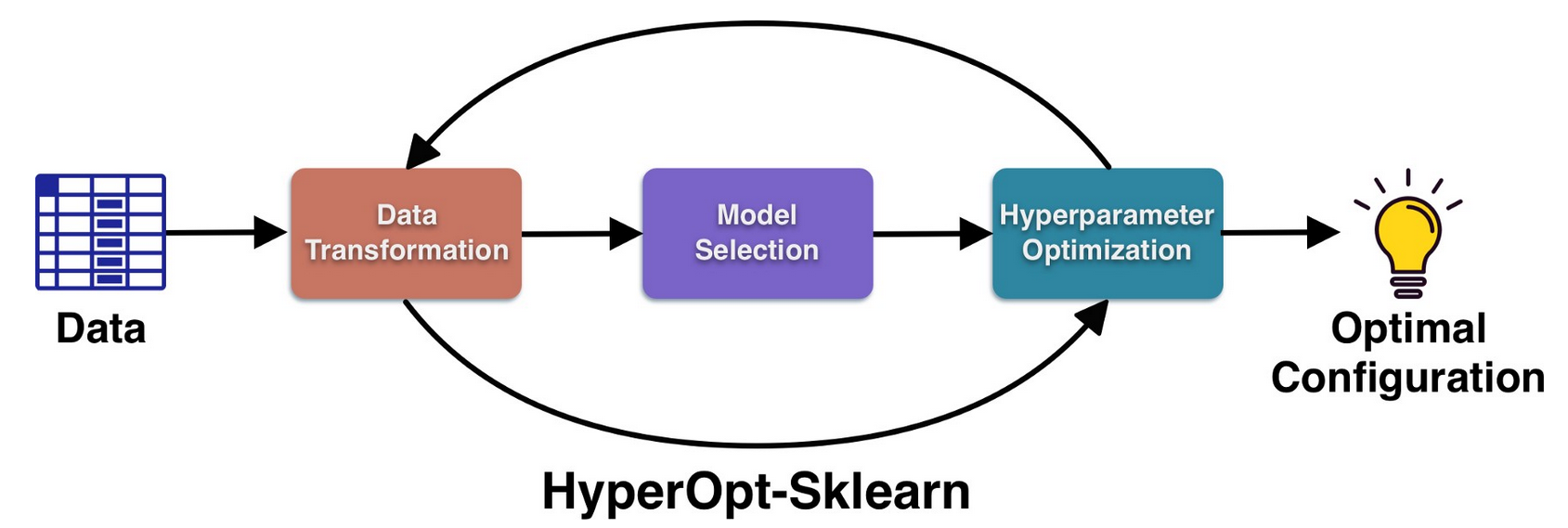 HyperOpt-Sklearn requires 3 essential parameters: the type of preprocessor, the machine learning model (i.e. classifier or regressor) and the optimizer. available preprocessor are: PCA, TfidfVectorizer, StandardScalar, MinMaxScalar, Normalizer, OneHotEncoder. available classification machine learning models are: SVC, LinearSVC KNeightborsClassifier, RandomForestClassifier, ExtraTreesClassifier SGDClassifier, MultinomialNB, BernoulliRBM, ColumnKMeans
HyperOpt-Sklearn requires 3 essential parameters: the type of preprocessor, the machine learning model (i.e. classifier or regressor) and the optimizer. available preprocessor are: PCA, TfidfVectorizer, StandardScalar, MinMaxScalar, Normalizer, OneHotEncoder. available classification machine learning models are: SVC, LinearSVC KNeightborsClassifier, RandomForestClassifier, ExtraTreesClassifier SGDClassifier, MultinomialNB, BernoulliRBM, ColumnKMeans
-
search across the entire spectrum of HyperOpt-Sklearn
```# HyperOpt-Sklearn from hpsklearn import HyperoptEstimator from hpsklearn import any_classifier from hpsklearn import any_preprocessing
# HyperOpt: Optimizer from hyperopt import tpe
# Sklearn stuff from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Load and split dataset x, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=23)
# Initialize Estimator # classifier: The search is done for the complete suite of classifiers # preprocessing: The preprocessing is donde for the complete suite of preprocessors # algo: Optimizer algorithm (Tree-structure of Parzen Trees) # max_evals: Number of iterations model = HyperoptEstimator(classifier=any_classifier(‘cla’), preprocessing=any_preprocessing(‘pre’), algo=tpe.suggest, max_evals=10, trial_timeout=30) # Training model.fit(x_train, y_train)
# Results print(f”Train score: {model.score(x_train, y_train)}”) print(f”Test score: {model.score(x_test, y_test)}”)
# Best model print(f”Optimal configuration: {model.best_model()}”)```
-
searching a single classifier with defined searchspace
```# HyperOpt-Sklearn from hpsklearn import HyperoptEstimator, sgd
# HyperOpt from hyperopt import hp
# Sklearn stuff from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split import numpy as np
# Load and split dataset x, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=23)
# Penalizer for SGD penalty = ‘l2’
# Search space of “loss functions” # Different loss variations are defined, each one # with an specific probability to be selected # In this case, “hinge” is prioritized with respect the others loss = hp.pchoice(‘loss’, [(0.50, ‘hinge’), (0.25, ‘log’), (0.25, ‘huber’)])
# Search space for alpha value is definied # with a log-uniform function alpha = hp.loguniform(‘alpha’, low=np.log(1e-5), high=np.log(1))
# Init Estimator # The classifier is passed with its respective hyperparameters model = HyperoptEstimator(classifier=sgd(‘my_sgd’, penalty=penalty, loss=loss, alpha=alpha), max_evals=10, trial_timeout=30)
# Training model.fit(x_train, y_train)
# Results print(f”Training score: {model.score(x_train, y_train)}”) print(f”Test score: {model.socre(x_test, y_test)}”)
# Optimal configuration print(f”Optimal configuration: {model.best_model()}”)```